
The first 10 Steps to significantly improve your KYC process
In the financial industry, the Know Your Customer (KYC) process is pivotal in mitigating risks and adhering to regulatory requirements. With technological advancements and increasing regulatory demands, enhancing your KYC procedures is essential. Our detailed guide outlines the first 10-steps to digitize and optimize your KYC operations, ensuring efficiency, compliance, and security.
Digital solutions, regulatory compliance, and advanced risk management techniques
Adopting the first 10 steps will not only refine your KYC processes but also position your organization at the forefront of digital innovation and regulatory compliance. By embracing digital solutions and advanced analytics, you can achieve a more secure, efficient, and compliant KYC procedure, essential for thriving in today’s dynamic financial environment.
Step 1: Digitization of Natural Person Identification
Initiate your KYC enhancement by digitizing information collection for individuals using tools like Microsoft Forms and Google Forms. This approach not only streamlines data gathering but also ensures adherence to GDPR and information security standards such as ISO/IEC 270XX and IT Grundschutz by BSI.
- Focus: Digitizing information collection using online forms.
- Tools: Microsoft Forms, Google Forms, DocuSign, etc.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 2: Advanced Verification Techniques
Employ digital verification tools like POSTIDENT Videochat and IDnow to authenticate identities reliably. Such platforms facilitate compliance with AML and counter-terrorist financing laws, backed by established standards like BaFin-Circular 3/2017 for video identification.
- Focus: Digitizing the verification process through video chat and other online verification tools.
- Tools: POSTIDENT Videochat, IDnow, webID.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 3: Beneficial Owner Identification
Clarify and digitize the identification of beneficial owners using Qualified Electronic Signature (QES), enhancing the transparency and security of transactions on behalf of natural persons.
- Focus: Digitizing the identification of beneficial owners.
- Tools: Qualified Electronic Signature (QES).
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 4: Legal Entity and Partnership Identification
Extend digitization to legal entities by collecting information through digital forms, ensuring GDPR compliance and safeguarding data integrity and security.
- Focus: Digitizing information collection for entities using online forms.
- Tools: Microsoft Forms, Google Forms, DocuSign, etc.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 5: Verification of Legal Entities
Integrate direct API connections to commercial and companies‘ registers for real-time verification of legal entities, improving the authenticity and reliability of collected data.
- Focus: Enhancing verification through direct API access to registers.
- Tools: APIs to commercial, trade, companies‘ registers.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 6: Unveiling Beneficial Owners of Legal Entities
Utilize sophisticated web crawlers and direct APIs to beneficial owner registers for in-depth analysis of ownership structures, significantly enhancing the quality and speed of information retrieval.
- Focus: Using web crawlers to collect information on beneficial owners from reliable sources.
- Tools: Sophisticated crawlers, direct API to beneficial owner registers.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 7: Business Relationship Analysis
Leverage big data analytics to assess the nature and purpose of business relationships, creating accurate customer risk profiles based on a wealth of mandatory and publicly available information.
- Focus: Digitizing the evaluation of business relationships using big data analytics.
- Tools: Big data analytics for customer risk profiling.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 8: Screening and Monitoring
Automate initial screenings for Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), sanctions, and other risk factors using supervised machine learning, streamlining alert and case management.
- Focus: Automating screening processes using machine learning for PEP/RCA and sanctions.
- Tools: Supervised machine learning.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 9: Customer Risk Rating Automation
Incorporate machine learning to automate customer risk assessments, facilitating dynamic and accurate risk profiling in line with evolving regulatory landscapes.
- Focus: Automating the customer risk rating process using machine learning.
- Tools: Supervised machine learning.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Step 10: Digital Record-Keeping
Employ knowledge graphs for efficient record-keeping, enabling a comprehensive visualization of all pertinent information related to business relationships, from customer data to transactions and beyond.
- Focus: Using knowledge graphs to digitize record-keeping and visualize business relationships.
- Tools: Knowledge graphs.
- Regulatory Attention: AML/ CTF Laws, Supervisory Authority Circulars, eIDAS-Regulation, GDPR, Information Security Guidelines, etc..
Analysis and Insights
In summary, the outlined 10 steps represent a first approach to modernizing the KYC process, emphasizing digital solutions, regulatory compliance, and advanced risk management techniques. This approach not only streamlines the KYC process but also enhances the accuracy and reliability of customer verification and monitoring, crucial for financial institutions in today’s rapidly evolving regulatory and technological landscape.
- Digital Transformation: The process heavily emphasizes digitizing the KYC process, reducing manual errors, and increasing efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Each step underscores the importance of adhering to GDPR and information security standards, ensuring that the process not only is efficient but also compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
- Security Focus: Attention to information security standards like ISO/IEC 270XX and IT Grundschutz highlights the importance of safeguarding personal and sensitive data throughout the KYC process.
- Innovative Tools and Techniques: The use of machine learning, knowledge graphs, and big data analytics indicates a forward-thinking approach, leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance the KYC process.
- Risk Management: Steps like customer risk rating and screening for PEP/RCA and sanctions are crucial for managing and mitigating risks associated with money laundering and financial crimes.
Practical experience
Drawing on over a decade of experience in the financial industry across a global canvas spanning 30 countries, we have witnessed a remarkable transformation in the operational efficiency of Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.
Corporate and Investment Banking (CIB)
In the realm of Corporate and Investment Banking (CIB), the KYC procedures have always been a critical but time-consuming endeavor. Reflecting on the days before optimization, handling KYC for low-risk clients could take up to two hours—a significant time investment reflecting the meticulous nature of the financial industry. Medium-risk clients demanded even more, three hours on average, while high-risk clients could occupy a whole four hours of meticulous review.
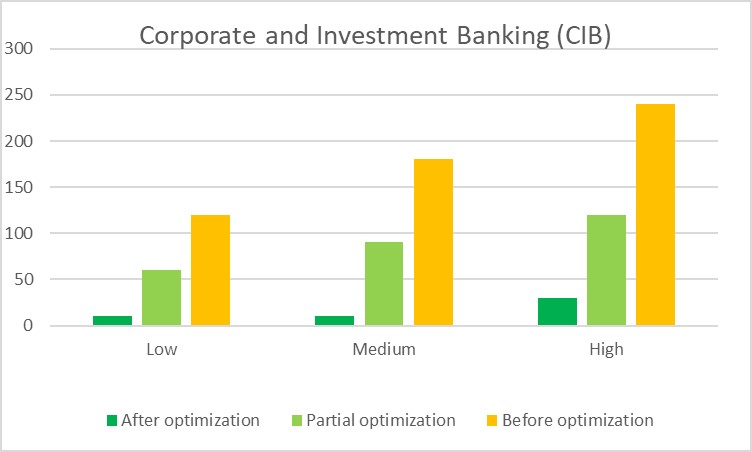
However, as the sector began embracing partial optimization, the winds of change brought about a notable decrease in handling times. Low-risk clients now required just an hour, medium-risk came down to an hour and a half, and high-risk clients needed two hours for a thorough review.
The true paradigm shift was realized after full optimization was implemented. The meticulous process that once spanned hours was condensed into mere minutes—10 minutes for both low and medium-risk clients, and a still impressive 30 minutes for high-risk clients. This quantum leap in efficiency wasn’t just about saving time; it was a testament to the industry’s adaptability and commitment to integrating cutting-edge technology and streamlined processes.
Retail Banking (RB)
Retail Banking (RB), with its direct consumer interactions, also underwent a similar transformative journey. Initially, low-risk KYC reviews could take two hours, with medium and high-risk reviews climbing to four and four and a half hours, respectively. Such extensive durations were not uncommon in the pre-digital era, where manual processes were the norm.
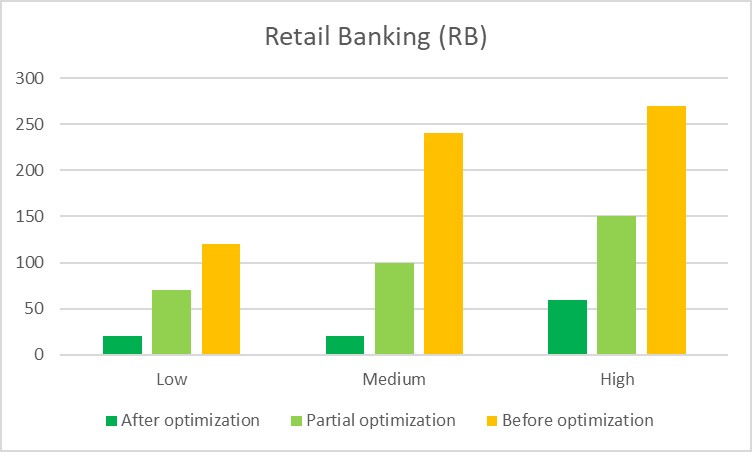
Partial optimization brought these times down considerably. Low-risk clients saw their KYC reviews shortened to a little over an hour, medium-risk to almost two hours, and high-risk to two and a half hours.
Post-optimization, the efficiency gains in RB were even more palpable. The process for low and medium-risk clients was streamlined to a swift 20 minutes, and high-risk clients were handled within an hour—a significant improvement that not only elevated operational efficiency but also enhanced customer satisfaction.
Three fictional case studies
The banking sector’s drive towards efficiency in Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures presents a compelling narrative of optimization potential. This narrative can be best understood through a comparative analysis of three distinct banking environments, each with its unique client base and risk profile distribution.
Assumptions:
- KYC must be carried out for all customers for the first time.
- A regular KYC Analyst in Germany works 1,783 hours per year or 34.3 hours per week on average.
- A regular KYC Analyst in Germany earns on average 47.100 € gross per year.
Notice:
- In reality, the customer base grows very slowly over many years.
- Most banks employ significantly fewer KYC analysts with a permanent full-time contract.
- Peaks in KYC reviews are often absorbed by temporary employment agencies.
Case Study 1: Small Retail Bank in the Countryside
With a relatively modest client base of 10,000, this small retail bank handles KYC reviews for 500 high-risk, 1,500 medium-risk, and 8,000 low-risk clients. Before optimization, the bank faces 120 hours for low-risk, 180 hours for medium-risk, and 240 hours for high-risk KYC processes cumulatively.
The introduction of partial optimization could reduce these figures to 70 hours for low-risk, 90 hours for medium-risk, and 150 hours for high-risk processes. Full optimization would streamline these processes further to an extraordinary 20 hours for low and medium-risk clients and 60 hours for high-risk clients. The potential for optimization here could lead to a paradigm shift, enabling this small bank to reallocate significant man-hours towards client engagement and business growth strategies.
Number of full-time employees (FTEs) required before and after optimization:
- Before Optimization:
- High Risk: 1.26 FTEs
- Medium Risk: 3.37 FTEs
- Low Risk: 8.97 FTEs
- Total FTEs Before Optimization: 13.60
- After Optimization:
- High Risk: 0.28 FTEs
- Medium Risk: 0.14 FTEs
- Low Risk: 0.75 FTEs
- Total FTEs After Optimization: 1.17
Annual cost in euros in Germany for the KYC analysts before and after optimization:
- Cost Before Optimization:
- High Risk: €59,436
- Medium Risk: €158,497
- Low Risk: €422,658
- Total Cost Before Optimization: €640,592
- Cost After Optimization:
- High Risk: €13,208
- Medium Risk: €6,604
- Low Risk: €35,222
- Total Cost After Optimization: €55,034
The first 10 steps as described above can already lead to a reduction in FTE and costs of up to 90%.
Case Study 2: Medium-Size Bank in a Large City
Servicing a substantial client roster of 100,000, this mid-tier bank in a metropolis navigates KYC reviews for 5,000 high-risk, 15,000 medium-risk, and 80,000 low-risk clients. Pre-optimization, the bank grapples with 120,000 hours for low-risk, 180,000 hours for medium-risk, and 270,000 hours for high-risk reviews in total.
With partial optimization, the total hours could be reduced to 70,000 for low-risk, 100,000 for medium-risk, and 150,000 for high-risk clients. Full optimization would revolutionize their processes to 20,000 hours across low and medium-risk segments and 60,000 hours for high-risk clients. The optimization potential for this bank is vast, with the possibility of repurposing tens of thousands of hours into enhancing customer service, compliance adherence, and operational excellence.
Number of full-time employees (FTEs) required before and after optimization:
- Before Optimization:
- High Risk: 12.62 FTEs
- Medium Risk: 33.65 FTEs
- Low Risk: 89.74 FTEs
- Total FTEs Before Optimization: 136.01
- After Optimization:
- High Risk: 2.80 FTEs
- Medium Risk: 1.40 FTEs
- Low Risk: 7.48 FTEs
- Total FTEs After Optimization: 11.68
Annual cost in euros in Germany for the KYC analysts before and after optimization:
- Cost Before Optimization:
- High Risk: €594,363
- Medium Risk: €1,584,969
- Low Risk: €4,226,584
- Total Cost Before Optimization: €6,405,917
- Cost After Optimization:
- High Risk: €132,081
- Medium Risk: €66,040
- Low Risk: €352,215
- Total Cost After Optimization: €550,337
The first 10 steps as described above can already lead to a reduction in FTE and costs of up to 90%.
Case Study 3: Large Corporate & Investment Bank (CIB) in a Capital
The largest of the trio, this CIB handles an extensive clientele of 1,000,000, including 50,000 high-risk, 150,000 medium-risk, and 800,000 low-risk clients. Initially, KYC reviews amass to 120,000,000 hours for low-risk, 180,000,000 hours for medium-risk, and 240,000,000 hours for high-risk cumulatively.
Through partial optimization, these daunting figures could be slashed to 70,000,000 for low-risk, 90,000,000 for medium-risk, and 150,000,000 for high-risk clients. However, the full optimization would usher in an unprecedented efficiency, cutting down the required hours to 20,000,000 for low and medium-risk, and 60,000,000 for high-risk clients. The optimization potential here transcends operational efficiency, potentially catalyzing industry-leading practices and significant cost savings at scale.
Number of full-time employees (FTEs) required before and after optimization:
- Before Optimization:
- High Risk: 126.19 FTEs
- Medium Risk: 336.51 FTEs
- Low Risk: 897.36 FTEs
- Total FTEs Before Optimization: 1,360.07
- After Optimization:
- High Risk: 28.04 FTEs
- Medium Risk: 14.02 FTEs
- Low Risk: 74.78 FTEs
- Total FTEs After Optimization: 116.84
Annual cost in euros in Germany for the KYC analysts before and after optimization:
- Cost Before Optimization:
- High Risk: €5,943,634
- Medium Risk: €15,849,692
- Low Risk: €42,265,844
- Total Cost Before Optimization: €64,059,170
- Cost After Optimization:
- High Risk: €1,320,808
- Medium Risk: €660,404
- Low Risk: €3,522,154
- Total Cost After Optimization: €5,503,365
The first 10 steps as described above can already lead to a reduction in FTE and costs of up to 90%.